How To Get Access Token From Service-account.json Java
The Google OAuth 2.0 system supports server-to-server interactions such every bit those between a web application and a Google service. For this scenario you need a service account, which is an account that belongs to your application instead of to an individual end user. Your application calls Google APIs on behalf of the service business relationship, so users aren't direct involved. This scenario is sometimes called "two-legged OAuth," or "2LO." (The related term "iii-legged OAuth" refers to scenarios in which your awarding calls Google APIs on behalf of end users, and in which user consent is sometimes required.)
Typically, an awarding uses a service account when the application uses Google APIs to work with its own data rather than a user'south data. For example, an application that uses Google Cloud Datastore for data persistence would use a service account to authenticate its calls to the Google Cloud Datastore API.
Google Workspace domain administrators tin can also grant service accounts domain-wide authority to admission user information on behalf of users in the domain.
This document describes how an awarding tin can complete the server-to-server OAuth ii.0 flow past using either a Google APIs client library (recommended) or HTTP.
Overview
To support server-to-server interactions, get-go create a service account for your project in the API Console. If you want to admission user information for users in your Google Workspace business relationship, then consul domain-wide access to the service account.
Then, your awarding prepares to make authorized API calls by using the service account's credentials to request an admission token from the OAuth 2.0 auth server.
Finally, your awarding can employ the access token to call Google APIs.
Creating a service business relationship
A service business relationship'south credentials include a generated electronic mail accost that is unique and at least one public/individual key pair. If domain-wide delegation is enabled, and so a client ID is also function of the service account'due south credentials.
If your application runs on Google App Engine, a service account is ready automatically when you create your project.
If your application runs on Google Compute Engine, a service account is also fix up automatically when you create your project, but you must specify the scopes that your awarding needs access to when you create a Google Compute Engine instance. For more information, see Preparing an case to use service accounts.
If your application doesn't run on Google App Engine or Google Compute Engine, yous must obtain these credentials in the Google API Console. To generate service-account credentials, or to view the public credentials that y'all've already generated, exercise the following:
Get-go, create a service account:
- Open up the Service accounts page.
- If prompted, select a project, or create a new one.
- Click Create service business relationship.
- Under Service account details, blazon a name, ID, and clarification for the service business relationship, then click Create and go on.
- Optional: Under Grant this service business relationship access to project, select the IAM roles to grant to the service account.
- Click Continue.
- Optional: Under Grant users access to this service account, add the users or groups that are allowed to utilize and manage the service account.
- Click Washed.
- Click Create key, then click Create.
Side by side, create a service account key:
- Click the email address for the service account you lot created.
- Click the Keys tab.
- In the Add key drop-downwards list, select Create new key.
- Click Create.
Your new public/private fundamental pair is generated and downloaded to your motorcar; it serves as the just copy of the private key. Y'all are responsible for storing it securely. If you lose this primal pair, you volition need to generate a new ane.
You can return to the API Console at any time to view the email address, public key fingerprints, and other data, or to generate boosted public/individual cardinal pairs. For more details about service account credentials in the API Panel, run across Service accounts in the API Console help file.
Have notation of the service account's electronic mail address and store the service account'south individual key file in a location accessible to your application. Your application needs them to make authorized API calls.
If you have a Google Workspace account, an ambassador of the organization tin can authorize an application to access user data on behalf of users in the Google Workspace domain. For example, an application that uses the Google Calendar API to add events to the calendars of all users in a Google Workspace domain would use a service account to access the Google Agenda API on behalf of users. Authorizing a service business relationship to access data on behalf of users in a domain is sometimes referred to every bit "delegating domain-wide authority" to a service account.
To consul domain-wide authorization to a service account, a super administrator of the Google Workspace domain must complete the following steps:
- From your Google Workspace domain'due south Admin panel,go to Main carte du jour > Security > API Controls.
- In the Domain wide delegation pane, select Manage Domain Wide Delegation.
- Click Add together new.
- In the Client ID field, enter the service account's Client ID. You tin detect your service account's client ID in the Service accounts folio.
- In the OAuth scopes (comma-delimited) field, enter the list of scopes that your application should exist granted access to. For case, if your application needs domain-wide full admission to the Google Bulldoze API and the Google Calendar API, enter: https://world wide web.googleapis.com/auth/bulldoze, https://www.googleapis.com/auth/agenda.
- Click Authorize.
Your awarding at present has the authorization to make API calls as users in your domain (to "impersonate" users). When you prepare to make authorized API calls, you specify the user to impersonate.
Preparing to make an authorized API call
Java
After yous obtain the client electronic mail accost and private key from the API Console, use the Google APIs Client Library for Java to create a GoogleCredential object from the service business relationship's credentials and the scopes your awarding needs access to. For example:
import com.google.api.client.googleapis.auth.oauth2.GoogleCredential; import com.google.api.services.sqladmin.SQLAdminScopes; // ... GoogleCredential credential = GoogleCredential.fromStream(new FileInputStream("MyProject-1234.json")) .createScoped(Collections.singleton(SQLAdminScopes.SQLSERVICE_ADMIN)); If you are developing an app on Google Cloud Platform, you can employ the application default credentials instead, which tin can simplify the process.
Delegate domain-wide authority
If you have delegated domain-wide access to the service account and you want to impersonate a user business relationship, specify the e-mail address of the user account with the createDelegated method of the GoogleCredential object. For instance:
GoogleCredential credential = GoogleCredential.fromStream(new FileInputStream("MyProject-1234.json")) .createScoped(Collections.singleton(SQLAdminScopes.SQLSERVICE_ADMIN)) .createDelegated("user@example.com"); Use the GoogleCredential object to phone call Google APIs in your awarding.
Python
Subsequently you lot obtain the customer email address and private cardinal from the API Console, use the Google APIs Customer Library for Python to complete the post-obit steps:
- Create a
Credentialsobject from the service account'southward credentials and the scopes your application needs access to. For example:from google.oauth2 import service_account SCOPES = ['https://www.googleapis.com/auth/sqlservice.admin'] SERVICE_ACCOUNT_FILE = '/path/to/service.json' credentials = service_account.Credentials.from_service_account_file( SERVICE_ACCOUNT_FILE, scopes=SCOPES)
If you lot are developing an app on Google Cloud Platform, you can employ the application default credentials instead, which tin simplify the process.
- Delegate domain-wide authorization
If yous take delegated domain-wide access to the service account and you want to impersonate a user account, use the
with_subjectmethod of an existingServiceAccountCredentialsobject. For case:delegated_credentials = credentials.with_subject('user@example.org')
Employ the Credentials object to telephone call Google APIs in your awarding.
HTTP/REST
After you obtain the client ID and private key from the API Console, your application needs to complete the following steps:
- Create a JSON Web Token (JWT, pronounced, "jot") which includes a header, a claim gear up, and a signature.
- Request an admission token from the Google OAuth 2.0 Authorization Server.
- Handle the JSON response that the Dominance Server returns.
The sections that follow describe how to complete these steps.
If the response includes an access token, yous can utilize the access token to call a Google API. (If the response does not include an access token, your JWT and token request might not be properly formed, or the service account might not have permission to access the requested scopes.)
When the access token expires, your application generates another JWT, signs it, and requests another access token.
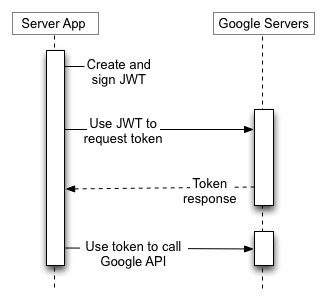
The rest of this section describes the specifics of creating a JWT, signing the JWT, forming the admission token request, and treatment the response.
Creating a JWT
A JWT is equanimous of three parts: a header, a claim set, and a signature. The header and claim ready are JSON objects. These JSON objects are serialized to UTF-8 bytes, so encoded using the Base64url encoding. This encoding provides resilience against encoding changes due to repeated encoding operations. The header, claim gear up, and signature are concatenated together with a period (.) character.
A JWT is equanimous as follows:
{Base64url encoded header}.{Base64url encoded claim prepare}.{Base64url encoded signature} The base of operations string for the signature is as follows:
{Base64url encoded header}.{Base64url encoded claim gear up} The header consists of two fields that indicate the signing algorithm and the format of the assertion. Both fields are mandatory, and each field has only one value. As additional algorithms and formats are introduced, this header will alter accordingly.
Service accounts rely on the RSA SHA-256 algorithm and the JWT token format. As a upshot, the JSON representation of the header is as follows:
{"alg":"RS256","typ":"JWT"} The Base64url representation of this is as follows:
eyJhbGciOiJSUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9
Forming the JWT claim set
The JWT merits set up contains information about the JWT, including the permissions being requested (scopes), the target of the token, the issuer, the time the token was issued, and the lifetime of the token. Most of the fields are mandatory. Like the JWT header, the JWT claim prepare is a JSON object and is used in the calculation of the signature.
Required claims
The required claims in the JWT claim set are shown beneath. They may announced in any lodge in the claim fix.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
iss | The email accost of the service account. |
scope | A space-delimited listing of the permissions that the application requests. |
aud | A descriptor of the intended target of the assertion. When making an access token request this value is always https://oauth2.googleapis.com/token. |
exp | The expiration time of the exclamation, specified equally seconds since 00:00:00 UTC, January 1, 1970. This value has a maximum of 1 hour afterward the issued time. |
iat | The time the assertion was issued, specified as seconds since 00:00:00 UTC, January one, 1970. |
The JSON representation of the required fields in a JWT claim set is shown below:
{ "iss": "761326798069-r5mljlln1rd4lrbhg75efgigp36m78j5@developer.gserviceaccount.com", "scope": "https://www.googleapis.com/auth/devstorage.read_only", "aud": "https://oauth2.googleapis.com/token", "exp": 1328554385, "iat": 1328550785 } Additional claims
In some enterprise cases, an application can utilize domain-wide delegation to act on behalf of a particular user in an organization. Permission to perform this blazon of impersonation must exist granted before an application tin can impersonate a user, and is unremarkably handled by a super administrator. For more information, come across Control API access with domain-wide delegation.
To obtain an access token that grants an application delegated access to a resource, include the e-mail address of the user in the JWT claim set equally the value of the sub field.
| Proper noun | Description |
|---|---|
sub | The e-mail address of the user for which the application is requesting delegated access. |
If an awarding does not accept permission to impersonate a user, the response to an admission token request that includes the sub field will be an error.
An example of a JWT merits gear up that includes the sub field is shown below:
{ "iss": "761326798069-r5mljlln1rd4lrbhg75efgigp36m78j5@developer.gserviceaccount.com", "sub": "some.user@example.com", "scope": "https://www.googleapis.com/auth/prediction", "aud": "https://oauth2.googleapis.com/token", "exp": 1328554385, "iat": 1328550785 } Encoding the JWT claim set
Like the JWT header, the JWT claim set should be serialized to UTF-viii and Base64url-safe encoded. Below is an example of a JSON representation of a JWT Claim ready:
{ "iss": "761326798069-r5mljlln1rd4lrbhg75efgigp36m78j5@developer.gserviceaccount.com", "scope": "https://www.googleapis.com/auth/prediction", "aud": "https://oauth2.googleapis.com/token", "exp": 1328554385, "iat": 1328550785 } Computing the signature
JSON Spider web Signature (JWS) is the specification that guides the mechanics of generating the signature for the JWT. The input for the signature is the byte array of the following content:
{Base64url encoded header}.{Base64url encoded claim set up} The signing algorithm in the JWT header must be used when calculating the signature. The only signing algorithm supported by the Google OAuth 2.0 Say-so Server is RSA using SHA-256 hashing algorithm. This is expressed as RS256 in the alg field in the JWT header.
Sign the UTF-eight representation of the input using SHA256withRSA (also known as RSASSA-PKCS1-V1_5-SIGN with the SHA-256 hash function) with the private key obtained from the Google API Console. The output will exist a byte array.
The signature must and then be Base64url encoded. The header, claim prepare, and signature are concatenated together with a period (.) grapheme. The issue is the JWT. It should be the following (line breaks added for clarity):
{Base64url encoded header}. {Base64url encoded merits set}. {Base64url encoded signature} Beneath is an example of a JWT before Base64url encoding:
{"alg":"RS256","typ":"JWT"}. { "iss":"761326798069-r5mljlln1rd4lrbhg75efgigp36m78j5@developer.gserviceaccount.com", "telescopic":"https://www.googleapis.com/auth/prediction", "aud":"https://oauth2.googleapis.com/token", "exp":1328554385, "iat":1328550785 }. [signature bytes] Below is an example of a JWT that has been signed and is gear up for manual:
eyJhbGciOiJSUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.eyJpc3MiOiI3NjEzMjY3OTgwNjktcjVtbGpsbG4xcmQ0bHJiaGc3NWVmZ2lncDM2bTc4ajVAZGV2ZWxvcGVyLmdzZXJ2aWNlYWNjb3VudC5jb20iLCJzY29wZSI6Imh0dHBzOi8vd3d3Lmdvb2dsZWFwaXMuY29tL2F1dGgvcHJlZGljdGlvbiIsImF1ZCI6Imh0dHBzOi8vd3d3Lmdvb2dsZWFwaXMuY29tL29hdXRoMi92NC90b2tlbiIsImV4cCI6MTMyODU1NDM4NSwiaWF0IjoxMzI4NTUwNzg1fQ.UFUt59SUM2_AW4cRU8Y0BYVQsNTo4n7AFsNrqOpYiICDu37vVt-tw38UKzjmUKtcRsLLjrR3gFW3dNDMx_pL9DVjgVHDdYirtrCekUHOYoa1CMR66nxep5q5cBQ4y4u2kIgSvChCTc9pmLLNoIem-ruCecAJYgI9Ks7pTnW1gkOKs0x3YpiLpzplVHAkkHztaXiJdtpBcY1OXyo6jTQCa3Lk2Q3va1dPkh_d--GU2M5flgd8xNBPYw4vxyt0mP59XZlHMpztZt0soSgObf7G3GXArreF_6tpbFsS3z2t5zkEiHuWJXpzcYr5zWTRPDEHsejeBSG8EgpLDce2380ROQ
Making the access token asking
After generating the signed JWT, an application tin use information technology to request an access token. This access token asking is an HTTPS POST request, and the body is URL encoded. The URL is shown below:
https://oauth2.googleapis.com/token
The following parameters are required in the HTTPS POST request:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
grant_type | Use the post-obit string, URL-encoded as necessary: urn:ietf:params:oauth:grant-type:jwt-bearer |
assertion | The JWT, including signature. |
Below is a raw dump of the HTTPS POST request used in an admission token asking:
POST /token HTTP/1.1 Host: oauth2.googleapis.com Content-Type: application/x-www-course-urlencoded grant_type=urn%3Aietf%3Aparams%3Aoauth%3Agrant-type%3Ajwt-bearer&assertion=eyJhbGciOiJSUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.eyJpc3MiOiI3NjEzMjY3OTgwNjktcjVtbGpsbG4xcmQ0bHJiaGc3NWVmZ2lncDM2bTc4ajVAZGV2ZWxvcGVyLmdzZXJ2aWNlYWNjb3VudC5jb20iLCJzY29wZSI6Imh0dHBzOi8vd3d3Lmdvb2dsZWFwaXMuY29tL2F1dGgvcHJlZGljdGlvbiIsImF1ZCI6Imh0dHBzOi8vYWNjb3VudHMuZ29vZ2xlLmNvbS9vL29hdXRoMi90b2tlbiIsImV4cCI6MTMyODU3MzM4MSwiaWF0IjoxMzI4NTY5NzgxfQ.ixOUGehweEVX_UKXv5BbbwVEdcz6AYS-6uQV6fGorGKrHf3LIJnyREw9evE-gs2bmMaQI5_UbabvI4k-mQE4kBqtmSpTzxYBL1TCd7Kv5nTZoUC1CmwmWCFqT9RE6D7XSgPUh_jF1qskLa2w0rxMSjwruNKbysgRNctZPln7cqQ
Beneath is the same asking, using ringlet:
curl -d 'grant_type=urn%3Aietf%3Aparams%3Aoauth%3Agrant-type%3Ajwt-bearer&assertion=eyJhbGciOiJSUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.eyJpc3MiOiI3NjEzMjY3OTgwNjktcjVtbGpsbG4xcmQ0bHJiaGc3NWVmZ2lncDM2bTc4ajVAZGV2ZWxvcGVyLmdzZXJ2aWNlYWNjb3VudC5jb20iLCJzY29wZSI6Imh0dHBzOi8vd3d3Lmdvb2dsZWFwaXMuY29tL2F1dGgvcHJlZGljdGlvbiIsImF1ZCI6Imh0dHBzOi8vYWNjb3VudHMuZ29vZ2xlLmNvbS9vL29hdXRoMi90b2tlbiIsImV4cCI6MTMyODU3MzM4MSwiaWF0IjoxMzI4NTY5NzgxfQ.RZVpzWygMLuL-n3GwjW1_yhQhrqDacyvaXkuf8HcJl8EtXYjGjMaW5oiM5cgAaIorrqgYlp4DPF_GuncFqg9uDZrx7pMmCZ_yHfxhSCXru3gbXrZvAIicNQZMFxrEEn4REVuq7DjkTMyCMGCY1dpMa8aWfTQFt3Eh7smLchaZsU ' https://oauth2.googleapis.com/token
Treatment the response
If the JWT and admission token request are properly formed and the service account has permission to perform the performance, and then the JSON response from the Potency Server includes an access token. The following is an instance response:
{ "access_token": "1/8xbJqaOZXSUZbHLl5EOtu1pxz3fmmetKx9W8CV4t79M", "telescopic": "https://www.googleapis.com/auth/prediction" "token_type": "Bearer", "expires_in": 3600 } Admission tokens can exist reused during the elapsing window specified past the expires_in value.
Calling Google APIs
Coffee
Use the GoogleCredential object to call Google APIs by completing the following steps:
- Create a service object for the API that you lot desire to call using the
GoogleCredentialobject. For example:SQLAdmin sqladmin = new SQLAdmin.Architect(httpTransport, JSON_FACTORY, credential).build();
- Brand requests to the API service using the interface provided by the service object. For example, to list the instances of Deject SQL databases in the exciting-example-123 project:
SQLAdmin.Instances.List instances = sqladmin.instances().listing("exciting-example-123").execute();
Python
Use the authorized Credentials object to call Google APIs by completing the following steps:
- Build a service object for the API that you want to call. Y'all build a a service object past calling the
buildfunction with the proper name and version of the API and the authorizedCredentialsobject. For example, to telephone call version 1beta3 of the Cloud SQL Administration API:import googleapiclient.discovery sqladmin = googleapiclient.discovery.build('sqladmin', 'v1beta3', credentials=credentials) - Brand requests to the API service using the interface provided by the service object. For example, to listing the instances of Deject SQL databases in the exciting-example-123 project:
response = sqladmin.instances().list(project='heady-example-123').execute()
HTTP/REST
Afterward your application obtains an access token, you can utilise the token to make calls to a Google API on behalf of a given service account or user account if the scope(southward) of admission required by the API accept been granted. To do this, include the access token in a request to the API by including either an access_token query parameter or an Authorisation HTTP header Bearer value. When possible, the HTTP header is preferable, because query strings tend to be visible in server logs. In about cases y'all can employ a customer library to ready upwards your calls to Google APIs (for example, when calling the Bulldoze Files API).
Y'all tin can try out all the Google APIs and view their scopes at the OAuth 2.0 Playground.
HTTP Get examples
A call to the drive.files endpoint (the Drive Files API) using the Potency: Bearer HTTP header might look similar the following. Note that you demand to specify your own admission token:
Become /drive/v2/files HTTP/1.ane Host: www.googleapis.com Authorization: Bearer access_token
Here is a call to the aforementioned API for the authenticated user using the access_token query string parameter:
Go https://www.googleapis.com/drive/v2/files?access_token=access_token
curl examples
You can test these commands with the curl command-line application. Hither'south an example that uses the HTTP header pick (preferred):
curlicue -H "Potency: Bearer access_token" https://www.googleapis.com/drive/v2/files
Or, alternatively, the query string parameter option:
ringlet https://www.googleapis.com/drive/v2/files?access_token=access_token
When access tokens elapse
Access tokens issued by the Google OAuth 2.0 Authority Server elapse after the duration provided past the expires_in value. When an access token expires, and then the awarding should generate another JWT, sign it, and request another access token.
JWT mistake codes
error field | error_description field | Meaning | How to resolve |
|---|---|---|---|
unauthorized_client | Unauthorized client or scope in request. | If you're trying to use domain-wide delegation, the service account is not authorized in the Admin console of the user's domain. | Ensure that the service account is authorized in the Domain-wide delegation page of the Admin console for the user in the While information technology usually takes a few minutes, it might take upwardly to 24 hours for authorization to propagate to all users in your Google Business relationship. |
unauthorized_client | Client is unauthorized to retrieve admission tokens using this method, or customer not authorized for any of the scopes requested. | A service account was authorized using the client email accost rather than the client ID (numeric) in the Admin console. | In the Domain-wide delegation page in the Admin console, remove the client, and re-add together it with the numeric ID. |
access_denied | (any value) | If you're using Domain-wide delegation, one or more requested scopes aren't authorized in the Admin console. | Ensure that the service account is authorized in the Domain-broad delegation folio of the Admin console for the user in the While it usually takes a few minutes, it might have upward to 24 hours for authorization to propagate to all users in your Google Account. |
invalid_grant | Not a valid email. | The user doesn't be. | Bank check that the email address in the sub claim (field) is correct. |
invalid_grant | | Usually, information technology means that the local system time is not right. It could likewise happen if the exp value is more than than 65 mins in the future from the iat value, or the exp value is lower than iat value. | Make sure that the clock on the organization where the JWT is generated is correct. If necessary, sync your time with Google NTP. |
invalid_grant | Invalid JWT Signature. | The JWT assertion is signed with a private central non associated with the service account identified by the client electronic mail or the key that was used has been deleted, disabled, or has expired. Alternatively, the JWT assertion might be encoded incorrectly - it must be Base64-encoded, without newlines or padding equal signs. | Decode the JWT claim prepare and verify the central that signed the assertion is associated with the service account. Effort to employ a Google-provided OAuth library to make sure the JWT is generated correctly. |
invalid_scope | Invalid OAuth scope or ID token audience provided. | No scopes were requested (empty list of scopes), or one of the requested scopes doesn't exist (i.e. is invalid). | Ensure that the Notation that the listing of scopes in the |
disabled_client | The OAuth client was disabled. | The key used to sign the JWT assertion is disabled. | Become to the Google API Console, and under IAM & Admin > Service Accounts, enable the service account which contains the "Central ID" used to sign the assertion. |
Annex: Service business relationship authorization without OAuth
With some Google APIs, you can make authorized API calls using a signed JWT direct as a bearer token, rather than an OAuth 2.0 access token. When this is possible, y'all tin can avoid having to make a network request to Google'due south authorization server before making an API call.
If the API you want to phone call has a service definition published in the Google APIs GitHub repository, yous can make authorized API calls using a JWT instead of an admission token. To practise then:
- Create a service account as described above. Be sure to keep the JSON file you get when you lot create the account.
- Using any standard JWT library, such as ane found at jwt.io, create a JWT with a header and payload like the post-obit example:
{ "alg": "RS256", "typ": "JWT", "kid": "abcdef1234567890" } . { "iss": "123456-compute@developer.gserviceaccount.com", "sub": "123456-compute@developer.gserviceaccount.com", "aud": "https://firestore.googleapis.com/", "iat": 1511900000, "exp": 1511903600 } - For the
kidfield in the header, specify your service account's private cardinal ID. Y'all can find this value in theprivate_key_idfield of your service account JSON file. - For the
issandsubfields, specify your service account's email accost. You can notice this value in theclient_emailfield of your service business relationship JSON file. - For the
audfield, specify the API endpoint. For example:https://SERVICE.googleapis.com/. - For the
iatfield, specify the current Unix time, and for theexpfield, specify the time exactly 3600 seconds later, when the JWT will expire.
Sign the JWT with RSA-256 using the private primal plant in your service account JSON file.
For case:
Coffee
Using google-api-java-client and java-jwt:
GoogleCredential credential = GoogleCredential.fromStream(new FileInputStream("MyProject-1234.json")); PrivateKey privateKey = credential.getServiceAccountPrivateKey(); String privateKeyId = credential.getServiceAccountPrivateKeyId(); long at present = System.currentTimeMillis(); try { Algorithm algorithm = Algorithm.RSA256(null, privateKey); String signedJwt = JWT.create() .withKeyId(privateKeyId) .withIssuer("123456-compute@programmer.gserviceaccount.com") .withSubject("123456-compute@developer.gserviceaccount.com") .withAudience("https://firestore.googleapis.com/") .withIssuedAt(new Date(now)) .withExpiresAt(new Appointment(now + 3600 * 1000L)) .sign(algorithm); } catch ... Python
Using PyJWT:
iat = time.fourth dimension() exp = iat + 3600 payload = {'iss': '123456-compute@programmer.gserviceaccount.com', 'sub': '123456-compute@developer.gserviceaccount.com', 'aud': 'https://firestore.googleapis.com/', 'iat': iat, 'exp': exp} additional_headers = {'kid': PRIVATE_KEY_ID_FROM_JSON} signed_jwt = jwt.encode(payload, PRIVATE_KEY_FROM_JSON, headers=additional_headers, algorithm='RS256') - Call the API, using the signed JWT as the bearer token:
Get /v1/projects/abc/databases/123/indexes HTTP/1.ane Authorization: Bearer SIGNED_JWT Host: firestore.googleapis.com
How To Get Access Token From Service-account.json Java,
Source: https://developers.google.com/identity/protocols/oauth2/service-account
Posted by: taylorshum1960.blogspot.com


0 Response to "How To Get Access Token From Service-account.json Java"
Post a Comment