How Data Interaction Happens Between 2 Micro Services
Microservices Communications
In this commodity, we're going to learn Microservices Communications. Nosotros volition learn definitions, communication types and how they can use in microservices architectures on e-commerce domain.
By the end of the article, you will larn Microservices Sync and Async Communications with patterns and practices. We will discuss RESTful APIs, gRPC and Message Broker systems.
Step by Step Design Architectures westward/ Course

I have just published a new course — Design Microservices Architecture with Patterns & Principles.
In this course, we're going to larn how to Design Microservices Architecture with using Design Patterns, Principles and the All-time Practices. We will start with designing Monolithic to Event-Driven Microservices stride by step and together using the right compages design patterns and techniques.
Microservices Communications
When we are talking virtually Monolithic applications, we said that the communication in Monolithic applications are inter-procedure communication. And then that means it is working on single procedure that invoke one to some other by using method calls. You simply create class and call the method within of target module. All running the same process.
This communication gives is very uncomplicated simply at the same fourth dimension components are highly coupled with each other and hard to separate and scale independently.
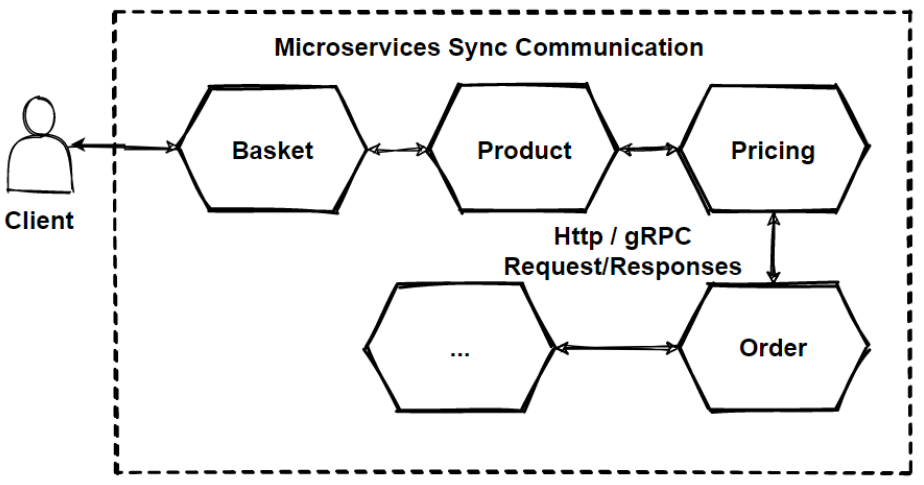
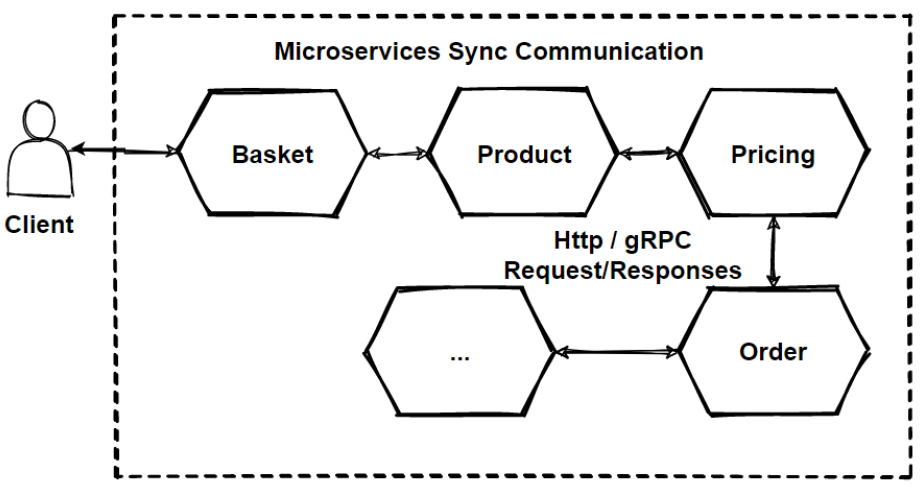
One of the biggest challenge when moving to microservices-based application is irresolute the communication machinery. Because microservices are distributed and microservices communicate with each other by inter-service advice on network level. Each microservice has its own instance and process. Therefore, services must collaborate using an inter-service advice protocols similar HTTP, gRPC or message brokers AMQP protocol.
Since microservices are complex structure into independently adult and deployed services, we should exist conscientious when considering communication types and manage them into design phases.
Before nosotros pattern our microservices communications, we should understand almost communication styles, it is possible to allocate them in two axes. The starting time footstep is to define advice protocol is synchronous or asynchronous.
Microservices Communication Types — Sync or Async Advice
We are going to acquire Microservices Communication types — Synchronous — Asynchronous Communication.
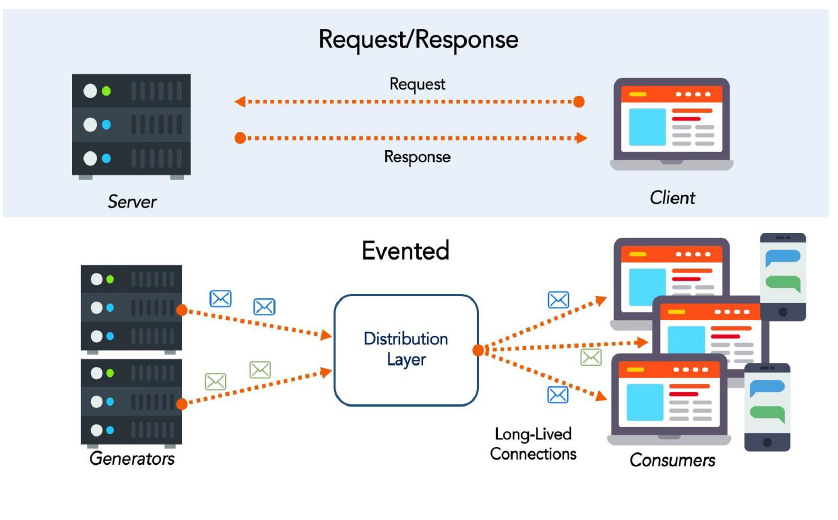
Client and services communicate with each other with many unlike types of advice. Mainly, those types of communications can be classified in 2 axes.
Synchronous and Asynchronous
Lets start to talk about Synchronous communication.
What is Synchronous communication ?
Basically, we tin can say that Synchronous communication is using HTTP or gRPC protocol for returning sync response. The client sends a request and waits for a response from the service. So that means client code block their thread, until the response reach from the server.
The synchronous advice protocols can be HTTP or HTTPS.
In synchronous communication, the client sends a asking with using http protocols and waits for a response from the service.
Then that means the client call the server and block client their operations.
The client lawmaking will keep its job when it receives the HTTP server response. So this operation called Synchronous communication. It has pros and cons that we should consider when we choice this manner.
Another communication blazon is Asynchronous communication.
What is Asynchronous advice ?
Basically, In Asynchronous communication, the client sends a request but information technology doesn't wait for a response from the service. So the key indicate here is that, the client should not have blocked a thread while waiting for a response.
The near popular protocol for this Asynchronous communications is AMQP (Avant-garde Bulletin Queuing Protocol). So with using AMQP protocols, the client sends the message with using message broker systems like Kafka and RabbitMQ queue. The message producer normally does not wait for a response. This bulletin consume from the subscriber systems in async way, and no one waiting for response suddenly.

An asynchronous communication also divided by 2 according to implementation. An asynchronous systems can be implemented in a ane-to-ane(queue) manner or ane-to-many (topic) mode.
In a one-to-ane(queue) implementation there is a single producer and single receiver. But in one-to-many (topic) implementation has Multiple receivers. Each request can be candy by zilch to multiple receivers. i-to-many (topic) communications must be asynchronous.
So nosotros will see this communication with the publish/subscribe mechanism used in patterns similar Event-driven microservices architecture in the upcoming manufactures. Basically an consequence-bus or bulletin broker system is publishing events between multiple microservices, and advice provide with subscribing these events in an async way.
Kafka and RabbitMQ is the best tools for this operations.
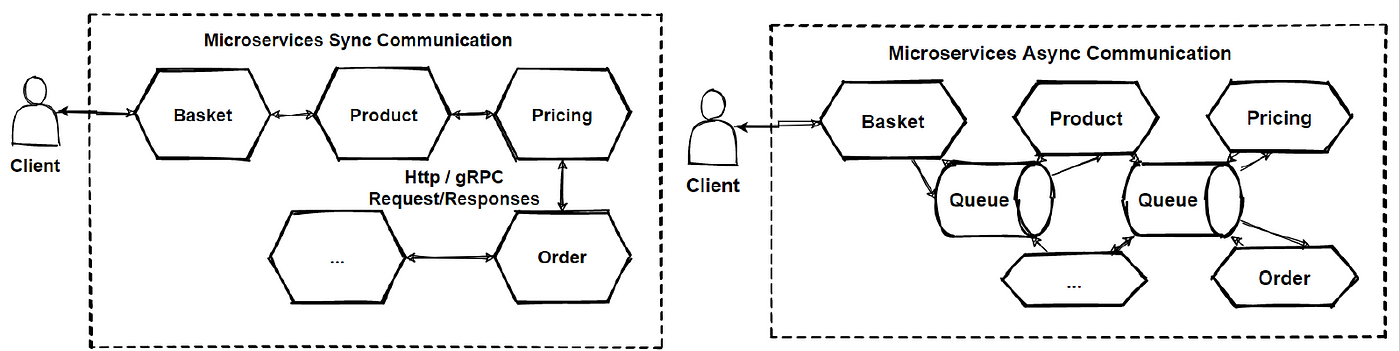
As you can come across that we have understand Microservices Advice types — Sync or Async Communication, And microservice-based application will often use a combination of these 2 advice styles. So we volition also pattern our e-commerce architecture with using both advice types.
But before that, lets elaborate the Synchronous advice and underlying mechanism.
Microservices Synchronous Advice and Practices
As we said before, In synchronous communication, the client sends a request with using http protocols and waits for a response from the service. The synchronous advice protocols tin be HTTP or HTTPS.
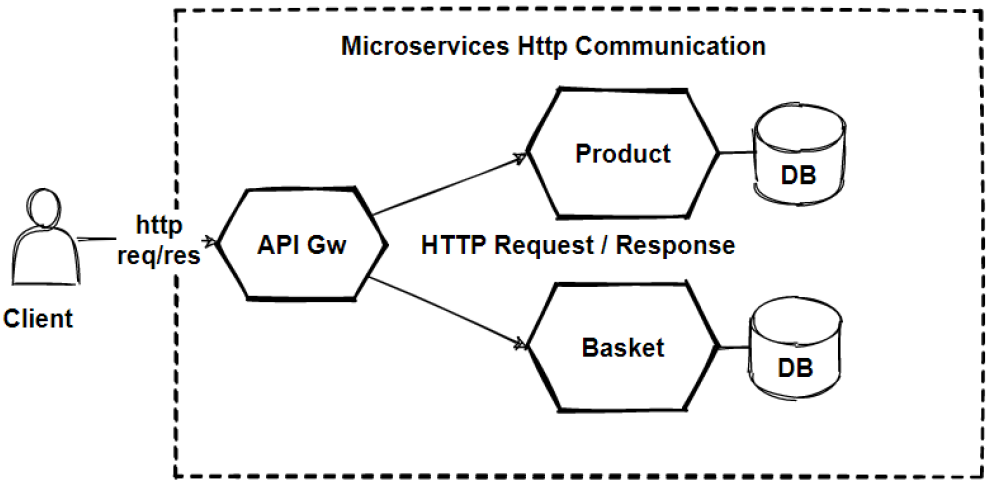
But how nosotros tin design and exposing APIs with HTTP protocols for our microservices ? we should focus on that signal.
When we are using a synchronous request/response-based communication type, HTTP protocols and Rest approaches are the well-nigh common way to use to design APIs, especially if we're exposing APIs to the outside of the microservice cluster.
If we're communicating betwixt services internally within our microservices cluster, we might likewise utilize binary format communication mechanisms like gRPC. gRPC is one of the all-time style to communicate for internal microservice advice, we volition run into gRPC in the upcoming sections.
E-Commerce Service Communications
Lets check our e-commerce architecture blueprint.

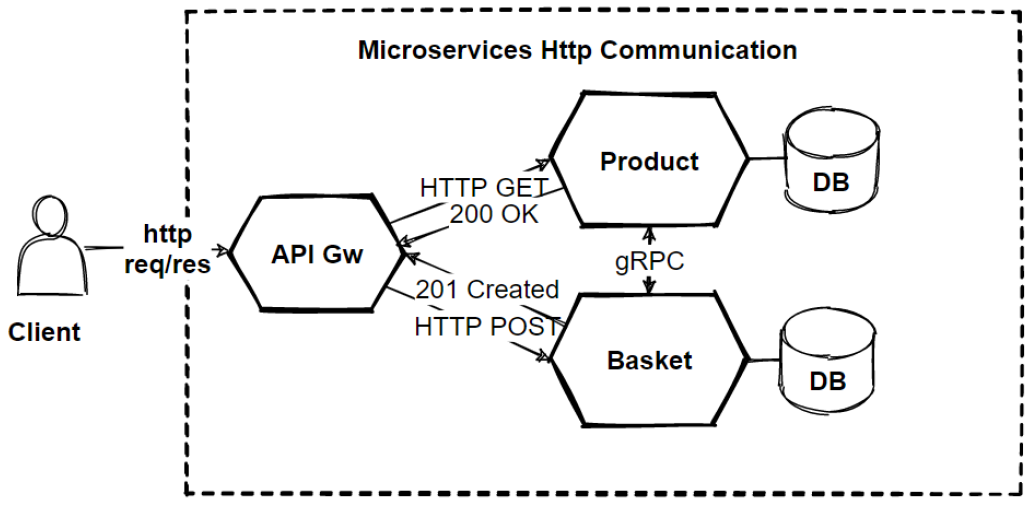
As you lot can come across that now these lines representing sync communication. And these communication will be HTTP based RESTful APIs which will return to JSON objects. Only if at that place is required to communicate internal microservices, its skilful to choose gRPC binary protocols in club to be fastest as posible.
Nosotros use dissimilar protocols for client phone call and the internal communication even both type is sync communication. Because customer request is good to be Residual in society to meet payloads explicitly, Just backend communication can be sacrifice to run into payloads instead of selection velocity of response fourth dimension. gRPC much faster than residuum.
And so we tin say that, if we prefer to communicate with synchronous communication, nosotros have several options those are; HTTP protocols and Remainder approaches. gRPC binary format communications.
So lets elaborate these ii approaches.
Designing HTTP based RESTful APIs for Microservices
In synchronous advice, when making request/response communication, we should apply Residual when designing our APIs. Its also called Restful APIs. REST arroyo is post-obit the HTTP protocol, and implementing HTTP verbs like GET, Postal service, and PUT.
Remainder is the most unremarkably used architectural communication approach when creating APIs for our microservices. For implementing REST services, we take several options for example using Java and Sprint Boot framework or using C# with ASP.NET Core Spider web API services.
Anyway, we should focus on how to blueprint our APIs for microservices.
Good API design is very important in a microservices architecture, considering advice with information transfers happens through messages or API calls.
Designed APIs should be efficient and not to be chatty communications. Because In microservices compages, services are designed for working independently, APIs must have well-defined documented and versioning, then updates don't pause other services.
At that place are 2 type of APIs when designing sync advice in microservices architecture.
i- Public APIs which is APIs calls from the client applications.
2- Backend APIs which is used for inter-service communication between backend microservices.
For Public APIs, should be align with customer asking. Clients can be web browser or mobile application requests. And then that means the public API should use RESTful APIs over HTTP protocol. So RESTful APIs should use JSON payloads for request-response, this will easy to check payloads and easy understanding with clients.
For the backend APIs, We demand to consider network performance instead of piece of cake readable JSON payloads. Inter-service advice can result in a lot of network traffic. For that reason, serialization speed and payload size become more important. So for the backend APIs, These protocols support binary serialization should implement. The protocol alternatives is using gRPC or other binary protocols are mandatory.
Let me compare the Rest and gRPC protocols,
REST is using HTTP protocol, and request-response structured JSON objects. API interfaces design based on HTTP verbs like Become-PUT-POST and DELETE.
gRPC is basically Remote Procedure Call, that basically invoke external system method over the binary network protocols. Payloads are not readable but its faster that Balance APIs.
So lets elaborate these 2 approaches.
- RESTful API Design over HTTP using JSON
- gRPC binary protocol API Blueprint
RESTful API design for Microservices
In synchronous advice, when making asking/response communication, we should use Residue when designing our APIs. Its besides called Restful APIs. Balance approach is post-obit the HTTP protocol, and implementing HTTP verbs similar Become, Mail service, and PUT.
RESTful services are widely used in modern Web architectures. Information technology is pretty lightweight, extensible and simple easy develop services. We will kickoff with Residue definition and later on that talk near RESTful Apis and how to pattern RESTFul Apis.
What is Residue ?
REST (Representational State Transfer) is a service structure that enables piece of cake and fast advice between client and server. Roy Fielding introduced and developed Residue in his doctoral thesis in 2000. Information technology was developed as an alternative to Lather and WSDL based Web services. REST runs on HTTP.
Compared to alternative structures, it is faster and more than efficient in sending and receiving data with more basic and minimum content. Balance allows applications to communicate with each other by carrying JSON data between the client and server.
Features of REST
When we expect at the constraints of the REST architecture, nosotros come beyond six items:
- Stateless
- Uniform Interface
- Cacheable
- Client-Server
- Layered System
- Code on Demand
I am not going to deep insight of these features but you can consider these are the characteristics of Residue services.
What is RESTful APIs?
Web services that utilise Residue architecture are called RESTful services. RESTful systems more often than not communicate over HTTP protocol with HTTP methods (Go, POST, PUT, DELETE etc.) used by Web Browsers to transfer pages.
Richardson Maturity Model
In 2008, Leonard Richardson proposed the Richardson Maturity Model for web APIs:
Level 0: Define one URI, and all operations are Postal service requests to this URI.
Level 1: Create separate URIs for individual resources.
Level 2: Use HTTP methods to define operations on resources.
Level 3: Utilise hypermedia
These are the levels of calculating maturity of REST APIs.
Lets understand the HTTP Methods which basically performs http operation over the APIs.

HTTP Methods
GET :
The Go method is used to fetch the resources specified in the URI. At that place is no body in this asking. It'south just the header. It is used for data listing and display operations. Requests made with Become must be secure. When data is sent with Become, information technology is sent in the address bar.
Postal service
Nosotros apply the Mail service method to create a new resources on the server. Nosotros send the asking in order to run the controller resources and to send the form inputs. Since nosotros will send data for all these operations, we also send the body when using the Mail service method. Information technology is used to add data and update existing information. Data is non displayed in the address bar, unlike the GET method.
PUT
The PUT method has a usage area like to the POST method. A resource is sent with the body and if the URI points to an existing resources, that resource is updated. Information technology is used to update information. Different from the POST method, the issue is the aforementioned even if the asking is repeated multiple times.
DELETE
As the proper noun suggests, it is the request sent to delete the resource specified in the URI. It is only used to delete the relevant resource and never be accessed again.
PATCH : Used to update a single piece of data.
How we can design Restful APIs for microservices ?
We should focus on the business concern entities that we betrayal APIs for our application. So that means we should organize our resources according to business organisation entities and expose them properly via APIs.
Lets think most our e-commerce awarding, the master entities might be customers and orders. When creating an order, nosotros basically send HTTP Mail request with contains customer and order detail data's. And return back to HTTP response that including 200 OK success response.
So how nosotros can handle this kind of Restful API ? The best exercise is the resource URIs should be based on nouns (the resource) and not verbs.
For instance :
https://eshop.com/orders // Right
https://eshop.com/create-order // Wrong
So now lets think about the e-commerce application and our Customer and Order entities, resource.
So if we design http methods, information technology should be on this table:
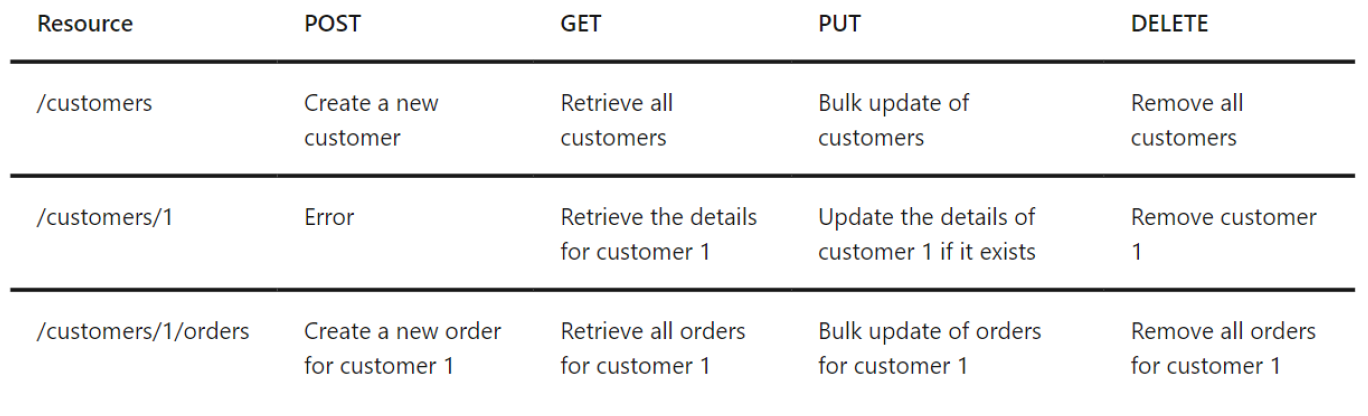
Since nosotros are using http protocol, You tin can discover Different Resource Urls are indicating with http verbs like get-put-mail and delete.
Meet the table we have /customers main resource. and we can filter past calculation /ane and /orders by post-obit REST principles.
Microservices RESTful API Design
If we talk virtually the microservices design on APIs you can meet the paradigm;
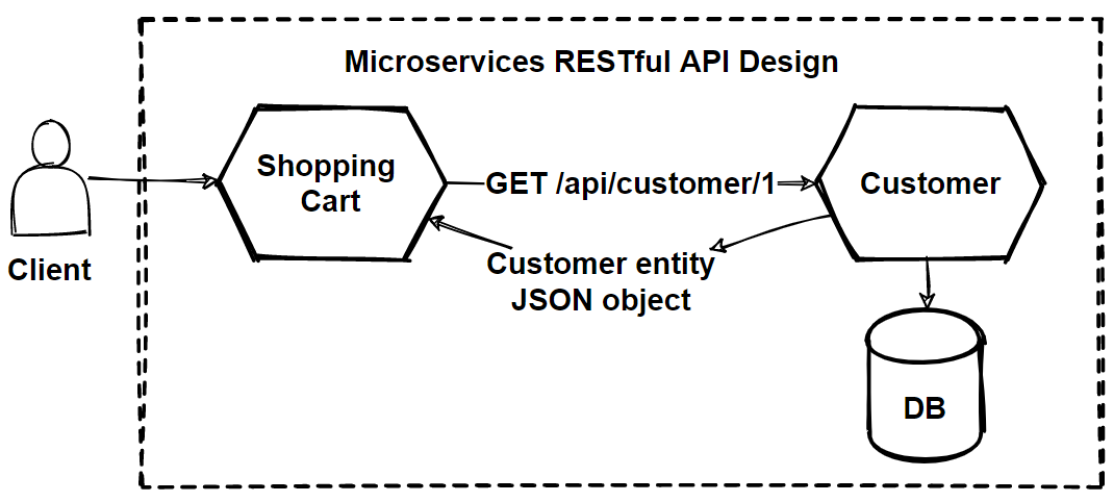
In a microservices architecture, microservices don't share the aforementioned code base and don't share data stores. Instead of that, they communicate through APIs for data operations.
If we look at the epitome, the Shopping Cart service requests information about a customer from the Customer service. The Customer service retrieve data with using Repository classes and render Customer entity model as a JSON object in an HTTP response. So this provide to isolation of services.
What is gRPC ?
gRPC (gRPC Remote Procedure Calls) is an open source remote process phone call (RPC) system initially developed at Google. gRPC is a framework to efficiently connect services and build distributed systems.

It is focused on loftier performance and uses the HTTP/2 protocol to transport binary letters. It is relies on the Protocol Buffers language to define service contracts. Protocol Buffers, also known every bit Protobuf, allow yous to define the interface to be used in service to service communication regardless of the programming language.
It generates cross-platform client and server bindings for many languages. About mutual usage scenarios include connecting services in microservices style architecture and connect mobile devices, browser clients to backend services. The gRPC framework allows developers to create services that can communicate with each other efficiently and independently from their preferred programming language.
Once you define a contract with Protobuf, this contract can exist used past each service to automatically generate the code that sets upwards the advice infrastructure. This feature simplifies the creation of service interaction and, together with high operation, makes gRPC the ideal framework for creating microservices.
How gRPC works ?
In GRPC, a customer awarding can directly phone call a method on a server application on a different motorcar like it were a local object, making it easy for y'all to build distributed applications and services.
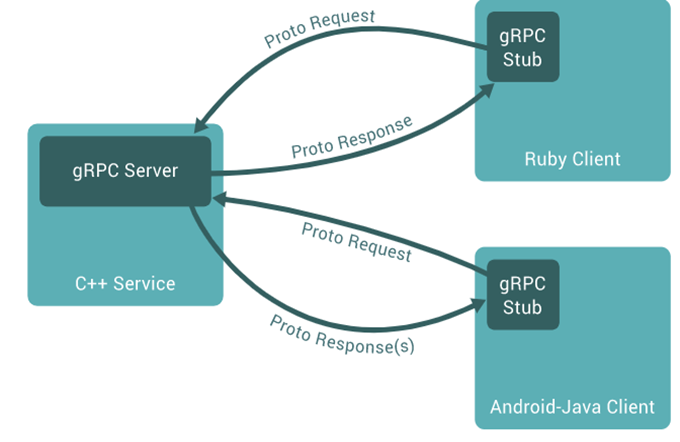
As with many RPC systems, gRPC is based on the thought of defining a service that specifies methods that can be called remotely with their parameters and return types. On the server side, the server implements this interface and runs a gRPC server to handle client calls. On the customer side, the client has a stub that provides the aforementioned methods as the server.
gRPC clients and servers tin work and talk to each other in a different of environments, from servers to your ain desktop applications, and that can be written in any language that gRPC supports. For case, you tin can hands create a gRPC server in Java or C# with clients in Go, Python or Reddish.
Working with Protocol Buffers
gRPC uses Protocol Buffers by Default. Protocol Buffers are Google's open source mechanism for serializing structured information.
When working with protocol buffers, the starting time footstep is to define the structure of the information yous want to serialize in a proto file: this is an ordinary text file with the extension .proto. The protocol buffer data is structured as messages where each message is a small logical information record containing a serial of name-value pairs called fields.
Once you've determined your information structures, you employ the protocol buffer compiler protocol to create data admission classes in the languages you prefer from your protocol definition.
Yous can detect the whole language guide into google'due south official documentation of protocol buffer language. Permit me add the link equally below.
https://developers.google.com/protocol-buffers/docs/overview
gRPC Method Types — RPC life cycles
gRPC lets you define four kinds of service method:
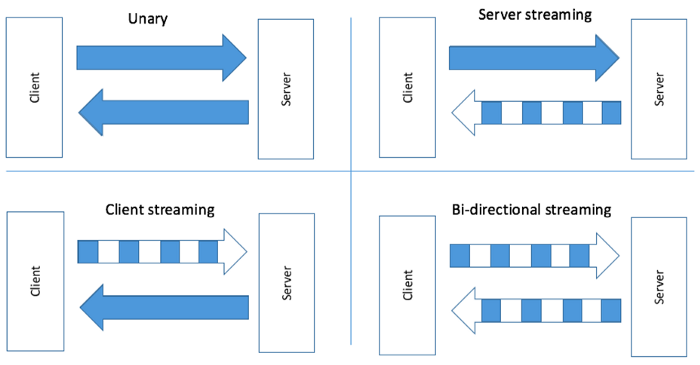
Unary RPCs where the client sends a unmarried asking to the server and returns a unmarried response dorsum, just like a normal part call.
Server streaming RPCs where the customer sends a request to the server and gets a stream to read a sequence of letters dorsum. The client reads from the returned stream until in that location are no more letters. gRPC guarantees message ordering inside an private RPC call.
Client streaming RPCs where the client writes a sequence of messages and sends them to the server, again using a provided stream. Once the client has finished writing the messages, it waits for the server to read them and return its response. Again gRPC guarantees message ordering inside an private RPC call.
Bidirectional streaming RPCs where both sides send a sequence of messages using a read-write stream. The two streams operate independently, so clients and servers tin read and write in whatever order they like: for example, the server could wait to receive all the client messages earlier writing its responses, or information technology could alternately read a message and so write a bulletin, or some other combination of reads and writes.
Advantages of gRPC
General advantages of gRPC:
- Using HTTP / 2
These differences of HTTP / ii provide xxx–twoscore% more than performance. In addition, since gRPC uses binary serialization, it needs both more performance and less bandwidth than json serialization.
- College performance and less bandwidth usage than json with binary serialization
- Supporting a wide audience with multi-linguistic communication / platform support
- Open up Source and the powerful community behind it
- Supports Bi-directional Streaming operations
- Support SSL / TLS usage
- Supports many Authentication methods
gRPC vs REST
gRPC is in an reward position against REST-based APIs that accept go popular in recent years. Considering of the protobuf format, messages take upwards less infinite and therefore communication is faster.
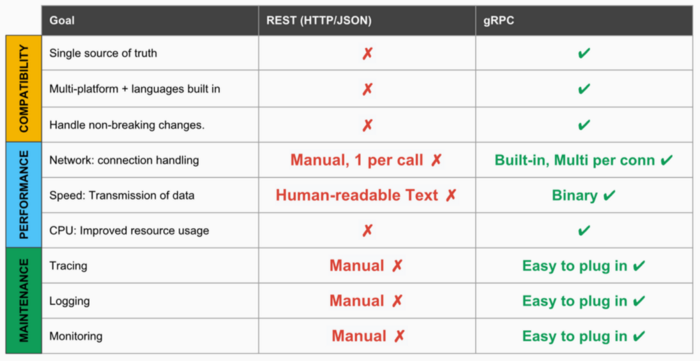
Dissimilar Remainder, gRPC works on a contract file footing, like to Soap.
Encoding and Decoding function of gRPC requests takes place on the client machine. That's why the JSON encode / decode you brand for REST apis on your machine is not a problem for you here.
You do not need to serialize (serialization / deserialization) for type conversions between different languages because your data type is clear on the contract and the code for your target language is generated from in that location.
gRPC usage of Microservices Communication
gRPC is primarily used with backend services.
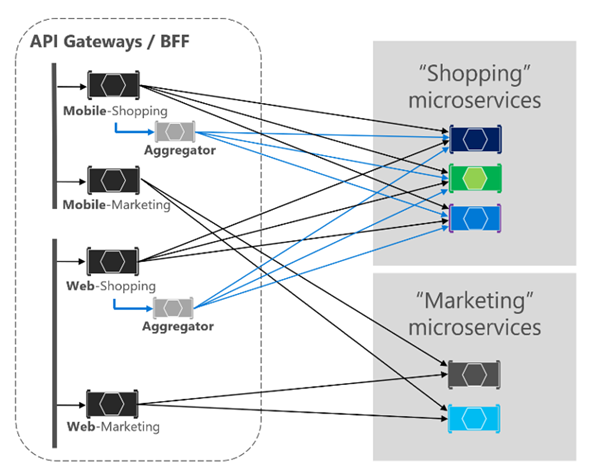
Only likewise gRPC using for the post-obit scenarios:
- Synchronous backend microservice-to-microservice communication where an firsthand response is required to proceed processing.
- Polyglot environments that need to support mixed programming platforms.
- Depression latency and high throughput communication where functioning is disquisitional.
- Point-to-bespeak existent-time communication — gRPC can button messages in real fourth dimension without polling and has excellent support for bi-directional streaming.
- Network constrained environments — binary gRPC messages are always smaller than an equivalent text-based JSON message.
Case of gRPC in Microservices Advice
Think virtually that nosotros have a Web-Marketing API Gateway and this will frontwards to request to Shopping Aggregator Microservice.
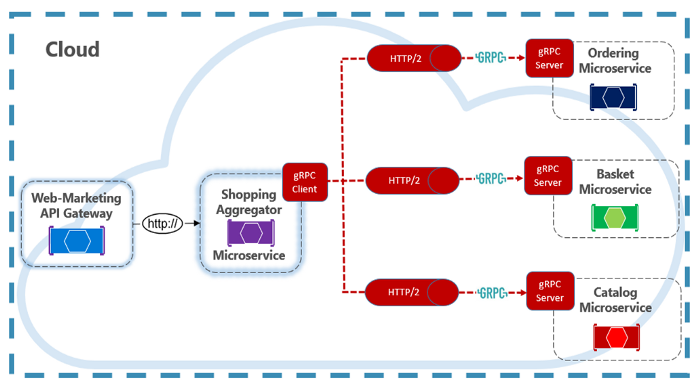
This Shopping Aggregator Microservice receives a single request from a client, dispatches it to various microservices, aggregates the results, and sends them back to the requesting client. Such operations typically crave synchronous advice every bit to produce an immediate response.
In this case, backend calls from the Aggregator are performed using gRPC. gRPC communication requires both customer and server components. You can run across that Shopping Aggregator implements a gRPC client. The client makes synchronous gRPC calls to backend microservices, this backend microservices are implement a gRPC server. As you tin see that, The gRPC endpoints must be configured for the HTTP/2 protocol that is required for gRPC advice.
In microservices earth, most of communication use asynchronous communication patterns but some operations crave direct calls. gRPC should be the primary choice for direct synchronous advice betwixt microservices. Its loftier-performance communication protocol, based on HTTP/2 and protocol buffers, make information technology a perfect option.
Drawbacks of the straight customer-to-microservices advice
We will compare the API gateway design and the Straight client-to-microservice communication. We take sympathize how to design Restful APIS for our microservices architecture. So for every microservices should exposes a fix of fine-grained endpoints to communicate each other.
In this view, each microservice has a public endpoint, and when we open public endpoint from our microservices, it has lots of drawbacks that we should consider.
When you build large and complex microservice-based applications for example, when treatment dozens of microservices, than these direct-to-microservices communication can brand bug.
The customer attempt to handle multiple calls to microservice endpoints but this is not manageable. Also if we call back that new microservices tin be add our application, its actually hard to manage those from the client application.

If we expand these problems; It can cause to lots of requests to the backend services and it can create possible communicative communications. This approach increases latency and complexity on the UI side. Ideally, responses should be aggregated in the server side.
Also implementing security and cross-cutting concerns like security and authorization for every microservice is not to practiced way of implementations. These cantankerous-cutting concerns should handle in centralized place that can be in internal cluster. Likewise if in that location is a long-running apis that demand to work on async communications, its hard to implement outcome-driven publish-subscribe model with message brokers from the client applications.
So these are the drawbacks of the direct client-to-microservices communication. Instead of that we should utilize API Gateways between client and internal microservices.
API Gateways can handle that Cross-cutting concerns like potency
so instead of writing every microservices, authorization can handle in centralized API gateways and sent to internal microservices.
Also API gateway manage routing to internal microservices and able to aggreate several microservice request in 1 response.
Then What's Next ?
Meet that UI and MS advice are direct, and it seems hard to manage communications. We now nosotros should focus on microservices communications with applying API GW pattern and evolving these architecture step past pace.
Step past Step Blueprint Architectures west/ Course

I have merely published a new course — Blueprint Microservices Architecture with Patterns & Principles.
In this class, we're going to acquire how to Design Microservices Compages with using Design Patterns, Principles and the Best Practices. We volition offset with designing Monolithic to Outcome-Driven Microservices step by step and together using the correct architecture design patterns and techniques.
References :
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-usa/azure/architecture/best-practices/api-design
https://denizirgin.com/rest-ve-restful-web-servis-kavram%C4%B1-30bc4400b9e0
https://wmaraci.com/nedir/balance-api
https://halilozel1903.medium.com/rest-ve-restful-nedir-f6c8596eb38a
How Data Interaction Happens Between 2 Micro Services,
Source: https://medium.com/design-microservices-architecture-with-patterns/microservices-communications-f319f8d76b71#:~:text=Because%20microservices%20are%20distributed%20and,or%20message%20brokers%20AMQP%20protocol.
Posted by: taylorshum1960.blogspot.com


0 Response to "How Data Interaction Happens Between 2 Micro Services"
Post a Comment